Virtual assessment based on root system architecture (RSA) modelling has great value in the optimisation of core-sampling strategies. Based on the measurement dataset of two maize cultivars having contrasting axile root angles, Wu et al. construct contrasting three-dimensional RSA models of individual maize plants in which the different lateral rooting angles are represented.
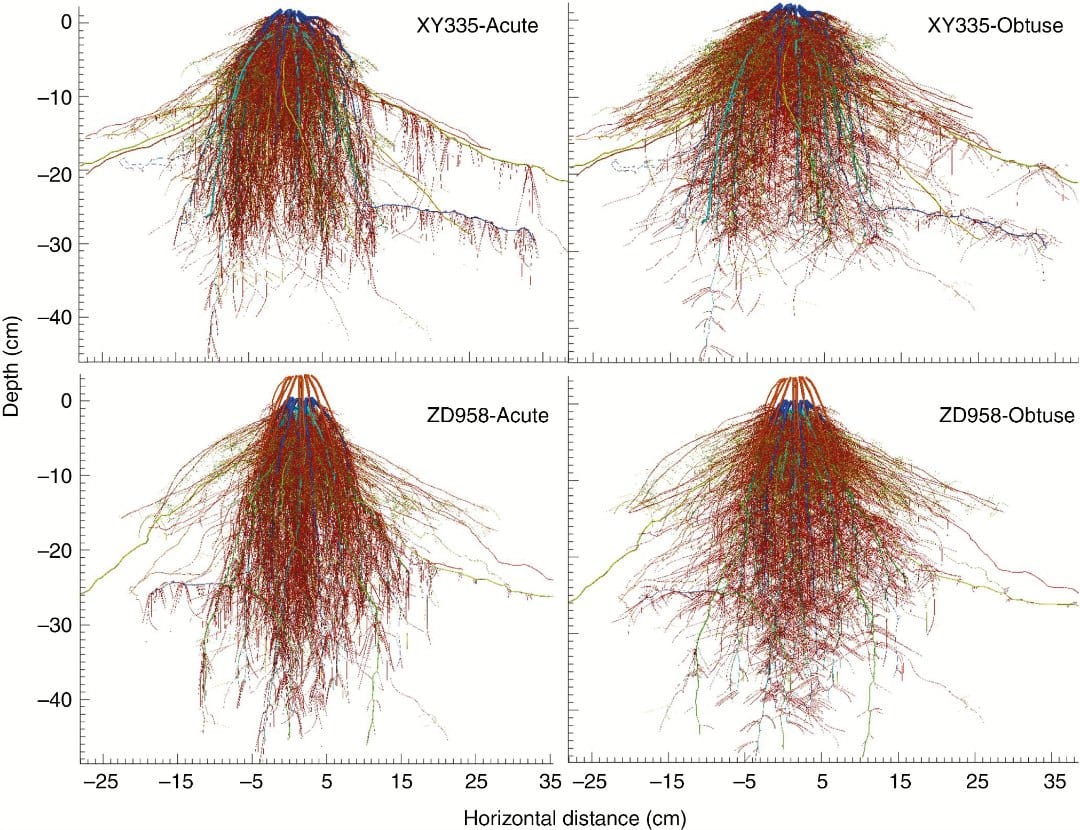
The accuracies of various core-sampling strategies for estimating root length density (RLD), including a new two-core sampling strategy based on an area-weighting algorithm, are assessed using these models. The new two-core sampling strategy shows considerable promise as a cost-efficient way of obtaining good-quality RLD estimates for maize.

This paper is part of the Annals of Botany Special Issue on Functional-Structural Plant Growth Modelling. It will be free access until June 2018, then available only to subscribers until April 2019 when it will be free access again.




